What are the Signs of Gum Disease?
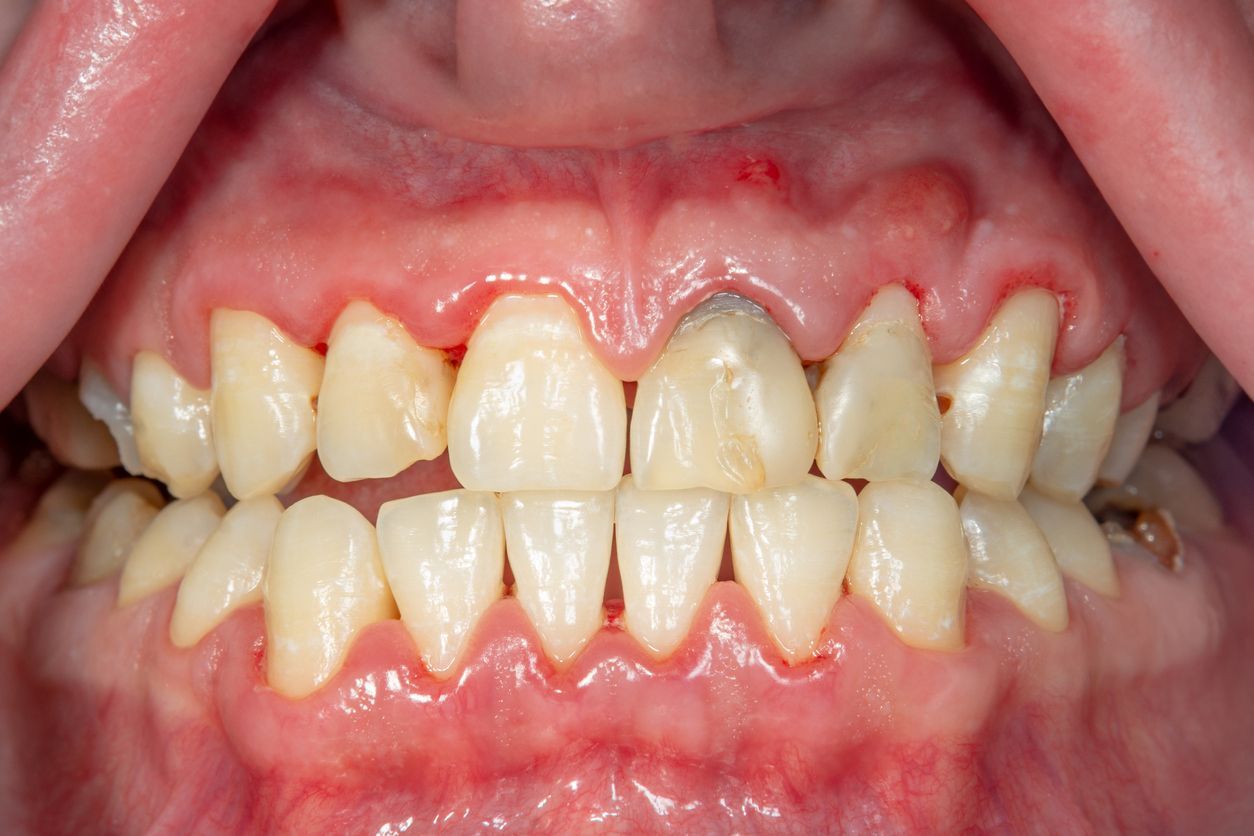
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a common but preventable condition that can have serious consequences for your oral and overall health if left untreated. Understanding the signs and symptoms of gum disease is crucial for early detection and treatment, helping to preserve your smile and well-being.
Understanding Gum Disease
Gum disease arises from infections and inflammation of the gums and bones that support your teeth. It is primarily caused by plaque, a sticky film of food debris, bacteria, and saliva. If plaque is not removed, it can harden into tartar, further exacerbating gum infection.
There are two main stages of gum disease: gingivitis, the milder form that affects only the gums, and periodontitis, a more severe condition that can damage the soft tissue and bone supporting the teeth.
Early Signs of Gum Disease
One of the first signs of gum disease is red, swollen, or tender gums that may bleed during brushing or flossing. These symptoms are often the body's response to plaque accumulation at the gumline. If noticed early, gingivitis can be reversed with professional dental cleaning and improved oral hygiene.
Advanced Symptoms of Gum Disease
As gum disease progresses to periodontitis, more alarming symptoms may emerge. Gums may begin to recede, pulling away from the teeth and creating pockets that harbor harmful bacteria. Teeth may become loose or shift, and persistent bad breath or a bad taste in the mouth can occur despite regular brushing and flossing.
Risk Factors and Prevention
Several factors can increase the risk of developing gum disease, including smoking, diabetes, hormonal changes in women, medications that reduce saliva flow, and genetic susceptibility. However, the most effective way to prevent gum disease is through regular dental check-ups, professional cleanings, and good oral hygiene practices such as brushing twice daily, flossing daily, and using antimicrobial mouthwash.
When to Seek Professional Care
Regular dental visits are essential for detecting gum disease in its early stages. During a check-up, your dentist or dental hygienist will examine your gums for signs of inflammation, measure the depth of any pockets around your teeth, and may take x-rays to assess bone loss. Early intervention can halt the progression of gum disease and minimize the need for more extensive treatment.
Conclusion
Recognizing the signs of gum disease is the first step toward maintaining a healthy mouth. If you experience any symptoms of gum disease, you'll need to consult your dentist as soon as possible for an evaluation and appropriate treatment. By prioritizing your oral health, you can prevent gum disease from advancing and ensure your teeth and gums remain healthy for years to come.
Call now to schedule your next appointment or set up a consultation!
FAQs: Understanding Gum Disease
What is the leading cause of gum disease?
The primary cause of gum disease is plaque buildup on the teeth. Plaque is a sticky film composed of bacteria, food particles, and saliva. If not removed through regular brushing and flossing, plaque can harden into tartar, leading to inflammation and infection of the gums.
Can gum disease affect overall health?
Yes, gum disease can impact overall health. Research has linked severe gum disease to various systemic conditions, including heart disease, diabetes, respiratory disease, and increased risk of stroke. The inflammation associated with gum disease may play a role in these connections.
Is gum disease reversible?
Gingivitis, the early stage of gum disease, is reversible with
proper oral hygiene and professional dental treatment. However, once gum disease progresses to periodontitis, the damage to the gums and bone is irreversible, though treatment can help manage the condition and prevent further deterioration.
How often should I visit the dentist to prevent gum disease?
Visiting the dentist for a check-up and professional cleaning at least twice a year is recommended. However, individuals with a higher risk of gum disease may need more frequent visits as their dentist advises.
What are the best ways to prevent gum disease?
The most effective ways to prevent gum disease include maintaining good oral hygiene practices, such as brushing teeth twice a day with fluoride toothpaste, flossing daily, using an antimicrobial mouthwash, and avoiding tobacco use. Regular dental check-ups and cleanings are also crucial for preventing gum disease.
Can smoking affect gum disease?
Yes, smoking is a significant risk factor for gum disease. Smokers are more likely to develop gum disease than non-smokers, and the condition tends to be more severe and less responsive to treatment in smokers.
What treatment options are available for gum disease?
Treatment options for gum disease vary depending on the severity of the condition. They can range from professional dental cleanings, scaling and root planing (a deep-cleaning procedure), antibiotics, to surgical interventions such as flap surgery or bone and tissue grafts for advanced cases.
Can gum disease lead to tooth loss?
Yes, if left untreated, gum disease can lead to tooth loss. Periodontitis, the advanced stage of gum disease, can destroy the bone and soft tissue supporting the teeth, eventually leading to tooth mobility and loss.
Is there a link between gum disease and pregnancy?
Pregnant women are at increased risk of developing gum disease due to hormonal changes that can affect the gums' response to plaque. Gum disease during pregnancy has been associated with premature birth and low birth weight, making it essential for pregnant women to pay particular attention to their oral health.
Can diet affect gum disease?
Yes, diet plays a role in oral health, including the risk of gum disease. A diet high in sugary foods and drinks can contribute to plaque formation, while a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals can help maintain healthy gums and teeth. What are the Signs of Gum Disease?
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a common but preventable condition that can have serious consequences for your oral and overall health if left untreated. Understanding the signs and symptoms of gum disease is crucial for early detection and treatment, helping to preserve your smile and well-being.
Understanding Gum Disease
Gum disease arises from infections and inflammation of the gums and bones that support your teeth. It is primarily caused by plaque, a sticky film of food debris, bacteria, and saliva. If plaque is not removed, it can harden into tartar, further exacerbating gum infection.
There are two main stages of gum disease: gingivitis, the milder form that affects only the gums, and periodontitis, a more severe condition that can damage the soft tissue and bone supporting the teeth.
Early Signs of Gum Disease
One of the first signs of gum disease is red, swollen, or tender gums that may bleed during brushing or flossing. These symptoms are often the body's response to plaque accumulation at the gumline. If noticed early, gingivitis can be reversed with professional dental cleaning and improved oral hygiene.
Advanced Symptoms of Gum Disease
As gum disease progresses to periodontitis, more alarming symptoms may emerge. Gums may begin to recede, pulling away from the teeth and creating pockets that harbor harmful bacteria. Teeth may become loose or shift, and persistent bad breath or a bad taste in the mouth can occur despite regular brushing and flossing.
Risk Factors and Prevention
Several factors can increase the risk of developing gum disease, including smoking, diabetes, hormonal changes in women, medications that reduce saliva flow, and genetic susceptibility. However, the most effective way to prevent gum disease is through regular dental check-ups, professional cleanings, and good oral hygiene practices such as brushing twice daily, flossing daily, and using antimicrobial mouthwash.
When to Seek Professional Care
Regular dental visits are essential for detecting gum disease in its early stages. During a check-up, your dentist or dental hygienist will examine your gums for signs of inflammation, measure the depth of any pockets around your teeth, and may take x-rays to assess bone loss. Early intervention can halt the progression of gum disease and minimize the need for more extensive treatment.
Conclusion
Recognizing the signs of gum disease is the first step toward maintaining a healthy mouth. If you experience any symptoms of gum disease, you'll need to consult your dentist as soon as possible for an evaluation and appropriate treatment. By prioritizing your oral health, you can prevent gum disease from advancing and ensure your teeth and gums remain healthy for years to come.
Contact your trusted dentist, Dr. Jeffrey Alvarado, at The Lake Family Dental in Edinburg, Texas.
(956) 680-6000
3103 Center Pointe Dr.
Edinburg, TX 78539


